Why Tattoo Ink is Permanent and the Best Ways to Remove Them
Why Tattoo Ink is Permanent and the Best Ways to Remove Them
Getting a tattoo can be an exciting and deeply personal experience. It allows individuals to express their uniqueness, tell a story, or simply adorn their bodies with beautiful artwork. However, as much as people love their tattoos, there may come a time when the need or desire for removal arises. Understanding why tattoo ink is permanent and exploring the best ways to remove them is important for those considering a change or a clean slate.
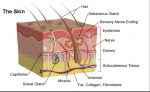
Tattoo ink permanence can be attributed to various factors. Firstly, the process of tattooing involves injecting ink into the dermis, the second layer of the skin, rather than the epidermis, which is the outermost layer that constantly sheds. The dermis is more stable and firmly holds the ink particles, making it difficult for the body to naturally remove them.
Moreover, the composition of tattoo ink contributes to its permanent nature. Traditional tattoo inks typically consist of pigments suspended in a carrier solution. The pigments mostly contain metal salts or mineral compounds that resist natural degradation. Some of these compounds include iron oxide, titanium dioxide, and carbon.
The size of the pigment particles is another significant factor. Small particles are more likely to be engulfed by immune cells called macrophages, which help in the process of tattoo fading over time. However, tattoo pigments are usually too large for macrophages to remove effectively. Instead, they become trapped in the dermal layer, leading to the long-lasting appearance of tattoos.
While tattoos are designed to be permanent, advancements in technology have made tattoo removal a reality. There are several methods available, each with its own pros and cons.
1. Laser Tattoo Removal:
This is the most common and effective method. Laser treatment uses high-intensity light to break down the ink particles into smaller fragments, allowing the body’s immune system to gradually remove them. Multiple sessions are typically required, depending on the tattoo’s size, color, and depth.
2. Tattoo Removal Creams:
Creams or ointments designed to lighten or remove tattoos can be found in the market. These products typically contain either skin-lightening chemicals or ingredients that exfoliate the skin. However, their effectiveness varies, and complete removal is rarely achieved without additional treatments.
3. Surgical Excision:
In this method, the tattoo is removed by cutting out the skin containing the tattoo and closing the remaining skin edges. Surgical excision may be appropriate for small tattoos but may result in scarring or loss of skin pigmentation.
4. Dermabrasion:
This technique involves abrasion of the tattooed skin using a brush or diamond wheel. This removes the upper layers of the skin, which contain the tattoo ink. Dermabrasion is generally used for smaller tattoos but may leave scars and often requires multiple sessions.
5. Intense Pulsed Light Therapy:
Similar to laser tattoo removal, this method uses intense pulses of light suited for certain colors. However, it is less effective than laser treatment and can result in an increased risk of scarring or skin discoloration.
The choice of tattoo removal method depends on various factors including tattoo size, color, location, and individual preferences. It is crucial to consult with a qualified dermatologist or tattoo removal specialist to determine the best course of action.
Why Tattoo Ink is Permanent and the Best Ways to Remove Them. In conclusion, tattoo ink is permanent due to its placement in the skin. While many people embrace their tattoos for life, circumstances and personal preferences may lead to the desire for removal. Thanks to advancements in tattoo removal technologies, individuals now have a range of methods to choose from. While none are entirely risk-free or guaranteed to rid all traces of a tattoo, laser tattoo removal remains the most effective and widely used option for those seeking significant fading or complete removal.